FastAPI 根据用户角色限流
限流
限流就是对请求进行控制和调度。这样做有助于防止系统负载过大导致崩溃或性能下降等情况。例如我可以对业务中核心的查询功能进行限流,保证这个接口一分钟最大允许100次请求(100/minutes)。
随着业务的调整,引入了会员机制,尊贵的人民币玩家可不能也"享受"着限流的待遇。但又不能全面放开导致接口被匿名未登录或者普通用户一样无限刷访问。于是需要对不同的角色进行不同的限流。
fastapi_limiter
调研fastapi限流库,Google搜索排名第一是fastapi-limiter,简单看了一下它的使用及文档,发现它的应用只局限于对接口的时间区间内的限制。
import redis.asyncio as redis
import uvicorn
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI
from fastapi_limiter import FastAPILimiter
from fastapi_limiter.depends import RateLimiter
app = FastAPI()
@app.on_event("startup")
async def startup():
redis = redis.from_url("redis://localhost", encoding="utf-8", decode_responses=True)
await FastAPILimiter.init(redis)
@app.get("/", dependencies=[Depends(RateLimiter(times=2, seconds=5))])
async def index():
return {"msg": "Hello World"}
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run("main:app", debug=True, reload=True)
它通过依赖绑定在接口中,并设置了5秒内只允许2次请求。
而它模块的核心实现是通过redis的lua脚本实现的,我对其做了详细的注释。
-- 获取传递给Lua脚本的第一个key。
local key = KEYS[1]
-- 从参数列表中获取限制数量,并将其转换为数字格式。
local limit = tonumber(ARGV[1])
-- 从参数列表中获取过期时间作为毫秒
local expire_time = ARGV[2]
-- 尝试从redis数据库读取当前计数器,如果不存在则返回0.
local current = tonumber(redis.call('get', key) or "0")
if current > 0 then
-- 如果当前计数器大于0,则将计数器加1
if current + 1 > limit then
-- 超过阈值,则返回redis键剩余生存时间
return redis.call("PTTL", key)
else
-- 未超过阈值,则将计数器加1
redis.call("INCR", key)
return 0
end
else
-- 初始化计数器,设置为1,并设置过期时间
redis.call("SET", key, 1, "px", expire_time)
return 0
end
以上lua脚本一旦返回值不为零,就意味着接口限制,返回值就是剩余时间。
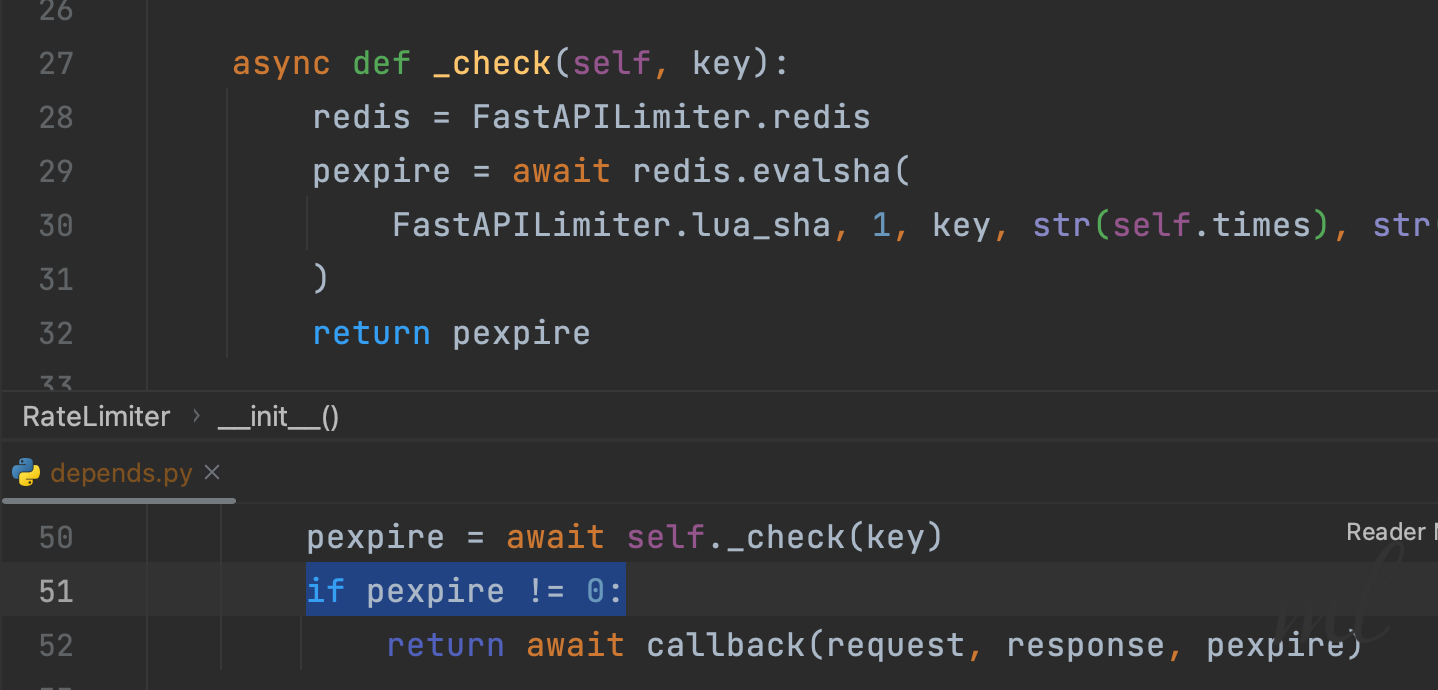
而事实上,源码中也是这么做的,一旦不为零,就触发异常的callback,在callback中返回HTTPException。
async def http_default_callback(request: Request, response: Response, pexpire: int):
expire = ceil(pexpire / 1000)
raise HTTPException(
HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS, "Too Many Requests", headers={"Retry-After": str(expire)}
)
在此模块的基础上,我们可以基于它的实现,封装对不同的角色进行不同的限流。
实现
首先,我们需要对不同的角色进行限流,那么我们需要知道当前请求的用户角色。往往项目中是通过jwt或者session来实现的,我这里简单使用headers中的token来模拟用户的角色。
class BaseUser:
rate_limit = None
class User(BaseUser):
"""普通已登录用户,十秒内允许5次请求"""
rate_limit = {
"times": 5,
"seconds": 10,
}
class AnonymousUser(BaseUser):
"""匿名未登录用户3秒只允许1次访问"""
rate_limit = {
"times": 1,
"seconds": 3,
}
class VIPUser(BaseUser):
"""vip用户,不限制请求"""
# mock当前用户
async def get_current_user(token=Header(None)):
if token is None:
return AnonymousUser()
if token == 'vip':
return VIPUser()
else:
return User()
class UserRateLimiter(RateLimiter):
"""
根据用户角色区分限流
"""
def __init__(self, times: conint(ge=0) = 1, milliseconds: conint(ge=-1) = 0, seconds: conint(ge=-1) = 0,
minutes: conint(ge=-1) = 0, hours: conint(ge=-1) = 0, identifier: Optional[Callable] = None,
callback: Optional[Callable] = None):
super().__init__(times, milliseconds, seconds, minutes, hours, identifier, callback)
self.times = times
self.seconds = seconds
self.minutes = minutes
self.hours = hours
self._milliseconds = milliseconds
@property
def milliseconds(self):
return self._milliseconds + 1000 * self.seconds + 60000 * self.minutes + 3600000 * self.hours
@milliseconds.setter
def milliseconds(self, value):
self._milliseconds = value
async def __call__(self, request: Request, response: Response, user=Depends(get_current_user)):
# 根据用户角色设置限流
if user.rate_limit:
for k, v in user.rate_limit.items():
setattr(self, k, v)
return await super().__call__(request, response)
我们将RateLimiter进行了封装,将times、seconds、minutes、hours等参数设置为可变的,然后根据用户角色设置限流。
根据对RateLimiter源码解读,主要是把时间归一化全部转为毫秒,然后给lua脚本传递参数,用于检查是否超过限制。
async def _check(self, key):
redis = FastAPILimiter.redis
pexpire = await redis.evalsha(
FastAPILimiter.lua_sha, 1, key, str(self.times), str(self.milliseconds)
)
return pexpire
所以,控制times和milliseconds就可以控制限流。
随后我们在接口上绑定UserRateLimiter,就可以实现对不同用户角色的限流了。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends
from fastapi_limiter import FastAPILimiter
from redis import asyncio
from depends.user_limiter import UserRateLimiter
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/", tags=["root"], dependencies=[Depends(UserRateLimiter())])
def root():
return "pass"
@app.on_event("startup")
async def startup():
pool = asyncio.ConnectionPool.from_url(
"redis://localhost",
encoding='utf-8',
decode_responses=True
)
redis = asyncio.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
await FastAPILimiter.init(redis)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app)
总结
本文我主要是我对fastapi_limiter的源码解读,以及如何基于它实现对不同用户角色的限流。思路其实很简单,区分角色,配置角色的限流,限流器根据角色的限流配置进行限流。